Supported cluster types
BigAnimal supports three cluster types:
- Single node
- Primary/standby high availability
- Distributed high availability
You choose the type of cluster you want on the Create Cluster page in the BigAnimal portal.
Single node
For nonproduction use cases where high availability isn't a primary concern, a cluster deployment with high availability not enabled provides one primary with no standby replicas for failover or read-only workloads.
In case of unrecoverable failure of the primary, a restore from a backup is required.

Primary/standby high availability
The Primary/Standby High Availability option is provided to minimize downtime in cases of failures. Primary/standby high-availability clusters—one primary and one or two standby replicas—are configured automatically, with standby replicas staying up to date through physical streaming replication.
If read-only workloads are enabled, then standby replicas serve the read-only workloads. In a two-node cluster, the single standby replica serves read-only workloads. In a three-node cluster, both standby replicas serve read-only workloads. The connections are made to the two standby replicas randomly and on a per-connection basis.
In cloud regions with availability zones, clusters are provisioned across zones to provide fault tolerance in the face of a datacenter failure.
In case of temporary or permanent unavailability of the primary, a standby replica becomes the primary.
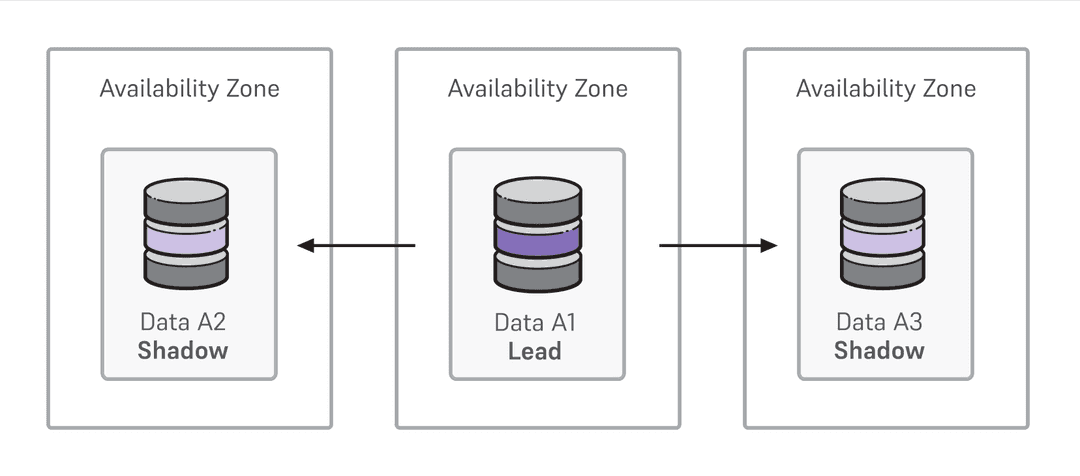
Incoming client connections are always routed to the current primary. In case of failure of the primary, a standby replica is promoted to primary, and new connections are routed to the new primary. When the old primary recovers, it rejoins the cluster as a standby replica.
Standby replicas
By default, replication is synchronous to one standby replica and asynchronous to the other. That is, one standby replica must confirm that a transaction record was written to disk before the client receives acknowledgment of a successful commit.
In a cluster with one primary and one replica (a two-node primary/standby high-availability cluster), you run the risk of the cluster being unavailable for writes because it doesn't have the same level of reliability as a three-node cluster. BigAnimal automatically disables synchronous replication during maintenance operations of a two-node cluster to ensure write availability. You can also change from the default synchronous replication for a two-node cluster to asynchronous replication on a per-session/per-transaction basis.
In PostgreSQL terms, synchronous_commit is set to on, and synchronous_standby_names is set to ANY 1 (replica-1, replica-2). You can modify this behavior on a per-transaction, per-session, per-user, or per-database basis with appropriate SET or ALTER commands.
To ensure write availability, BigAnimal disables synchronous replication during maintenance operations of a two-node cluster.
Since BigAnimal replicates to only one node synchronously, some standby replicas in three-node clusters might experience replication lag. Also, if you override the BigAnimal synchronous replication configuration, then the standby replicas are inconsistent.
Distributed high availability
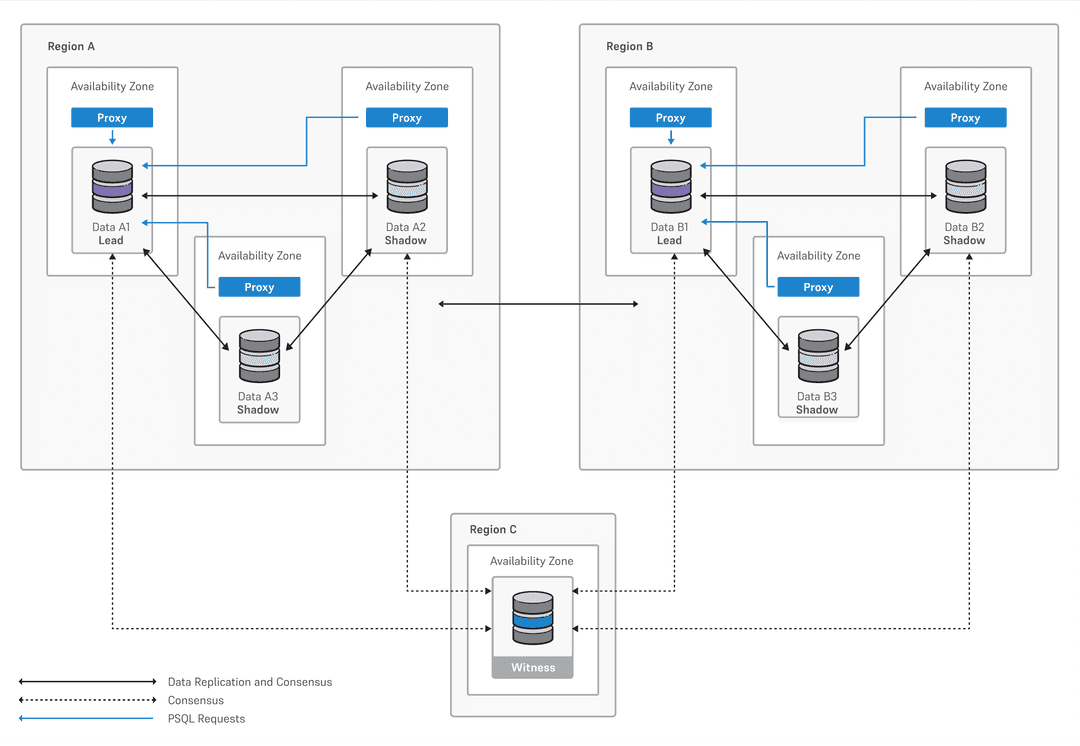
Distributed high-availability clusters are powered by EDB Postgres Distributed using multi-master logical replication to deliver more advanced cluster management compared to a physical replication-based system. Distributed high-availability clusters offer the ability to deploy a cluster across multiple regions or a single region. For use cases where high availability across regions is a major concern, a cluster deployment with distributed high availability enabled can provide one region with three data nodes, another region with the same configuration, and one group with a witness node in a third region for a true active-active solution.
Distributed high-availability clusters support both EDB Postgres Advanced Server and EDB Postgres Extended Server database distributions.
Distributed high-availability clusters contain one or two data groups. Your data groups can contain either three data nodes or two data nodes and one witness node. One of these data nodes is the leader at any given time, while the rest are shadow nodes. We recommend that you don't use two data nodes and one witness node in production unless you use asynchronous commit scopes.
PGD Proxy routes all application traffic to the leader node, which acts as the principal write target to reduce the potential for data conflicts. PGD Proxy leverages a distributed consensus model to determine availability of the data nodes in the cluster. On failure or unavailability of the leader, PGD Proxy elects a new leader and redirects application traffic. Together with the core capabilities of EDB Postgres Distributed, this mechanism of routing application traffic to the leader node enables fast failover and switchover.
The witness node/witness group doesn't host data but exists for management purposes, supporting operations that require a consensus, for example, in case of an availability zone failure.
Note
Operations against a distributed high-availability cluster leverage the EDB Postgres Distributed switchover feature which provides sub-second interruptions during planned lifecycle operations.
Single data location
A single data location configuration has three data nodes with one lead and two shadow nodes each in separate availability zones.
Two data locations and witness
A true active-active solution that protects against regional failures, a two data locations configuration has:
A data node, shadow node, and a witness node in one region
The same configuration in another region
A witness node in a third region
For more information
For instructions on creating a distributed high-availability cluster using the BigAnimal portal, see Creating a distributed high-availability cluster.
For instructions on creating, retrieving information from, and managing a distributed high-availability cluster using the BigAnimal CLI, see Using the BigAnimal CLI.